Table Of Content
- Characteristics of Pre-experimental Designs
- Types of Experimental Research Designs
- Insufficient or Incorrect Statistical Analysis
- You are unable to access scribbr.com
- Types of Pre-experimental Designs
- This Prefab Builder Is Making Homes That Are Designed to Keep You Healthy
- Exploratory and Confirmatory Research
This sums up the basics of pre-experimental design and how it differs from other experimental research designs. Curious to learn how you can use survey software to conduct your experimental research, book a meeting with us. The pre-experimental design includes one or more than one experimental groups to be observed against certain treatments. It is the simplest form of research design that follows the basic steps in experiments. To publish significant results, choosing a quality research design forms the foundation to build the research study. Moreover, effective research design helps establish quality decision-making procedures, structures the research to lead to easier data analysis, and addresses the main research question.
Characteristics of Pre-experimental Designs
Through this semistructured process, they were able to identify trends in expert opinion, as well as rank the trends to help inform public policy. Due to such working, static-group comparison design is generally perceived as a quasi-experimental design too. Randomization is important in an experimental research because it ensures unbiased results of the experiment. By creating a research design, a researcher is also giving oneself time to organize the research, set up relevant boundaries for the study, and increase the reliability of the results.
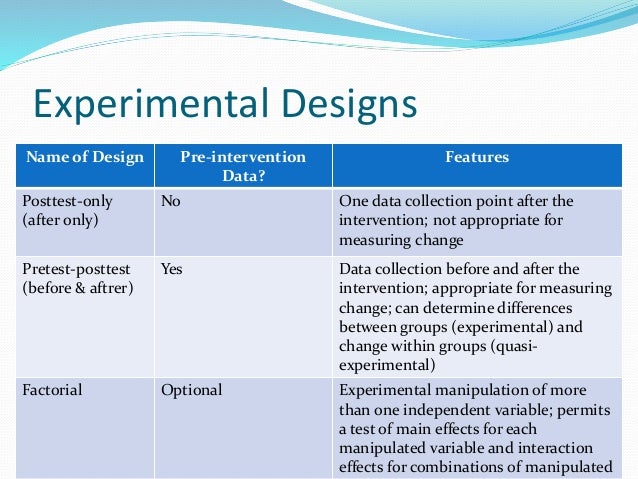
Types of Experimental Research Designs
[1] The nonequivalent comparison group design looks a lot like the classic experimental design, except it does not use random assignment. Perhaps the treatment group has a characteristic that is unique–for example, higher income or different diagnoses–that make the treatment more effective. Quasi-experimental designs have a comparison group that is similar to a control group except assignment to the comparison group is not determined by random assignment. The nonequivalent comparison group design looks a lot like the classic experimental design, except it does not use random assignment. While this method is more convenient for real-world research, it is less likely that that the groups are comparable than if they had been determined by random assignment. Researchers who conduct hypothesis testing in vivo animal work should understand the importance of limiting the impact of experimental biases in the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of in vivo experiments.
Insufficient or Incorrect Statistical Analysis
As illustrated by the Ludwig and Miller study, the design can be used when individual participants, neighborhoods, cities, or counties are the unit of assignment. When new programs are implemented, assignment on the basis of need or risk may be more acceptable to communities that may be resistant to RCTs. The use of a clinically meaningful quantitative assignment variable (e.g., risk level) may help overcome ethical or political objections when a promising potential treatment is being evaluated. Given that the design can often be implemented with the full population of interest—a state, community, school, or hospital—it provides direct evidence of population-level effects.
A safe and effective micro-choice based rehabilitation for patients with long COVID: results from a quasi-experimental ... - Nature.com
A safe and effective micro-choice based rehabilitation for patients with long COVID: results from a quasi-experimental ....
Posted: Fri, 09 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
In this instance, pre- and posttests are both taken, but there is no control group to which to compare the experimental group. Because there is no pretest and no comparison group, this design is not useful for supporting causality since we can’t establish time order and we can’t control for extraneous variables. Sometimes, agencies need to gather information about how their programs are functioning. A classic example of this design is satisfaction surveys—realistically, these can only be administered after a program or intervention. Questions regarding satisfaction, ease of use or engagement, or other questions that don’t involve comparisons are best suited for this type of design. Also known as a before-after one-group design, this type of research design does not have a comparison group; everyone who participates in the research receives the intervention or is exposed to the experimental condition (Figure 14.8).
Yet it is widely used in research institutes and commercial industries, for its most conclusive results in the scientific approach. The ultimate goal of a research experiment is to gain valid and sustainable evidence. Therefore, incorrect statistical analysis could affect the quality of any quantitative research. In this article, we will not only discuss the key aspects of experimental research designs but also the issues to avoid and problems to resolve while designing your research study.
Imagine if the students in your research class completed a questionnaire about their level of stress at the beginning of the semester. If there was a comparison group, she would be able to recognize that all students experienced higher stress at the end of the semester than the beginning of the semester, not just the students in her research class. Mapping refers to tracing the causal chains or mechanisms of change inferred when evidence is matched with levels of intervention and change. The evidence will be incomplete at each ecological level with respect to the local or state circumstances in which a decision and action must be taken, but theory can (and will, formally or informally, consciously or unconsciously) be brought to bear.
Ideally, these protocols should be preregistered and/or published, so that the methods which will be used to reduce the impact of bias are documented in an a priori fashion. The process of peer review of a protocol prior to initiating experiments of course is a valuable opportunity for refinement and improvement. Registering protocols encourages rigour and transparency, even if the protocol is not peer-reviewed. Some journals are open to submissions of these types of protocols, such as BMJ Open Science, and many journals offer the Registered Reports format.
Exploratory and Confirmatory Research
What we cannot say is if this change would have occurred even without the application of the treatment or independent variable. It is possible that mere maturation caused the change in grades and not the work experience itself. To illustrate, the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) allowed television broadcasting to be introduced for the first time in several medium-sized cities in the United States in 1951. Bans on indoor smoking have been introduced in numerous cities (and states) on specific dates. If outcome data can be collected or archival data are available at regular fixed intervals (e.g., weekly, monthly), the ITS provides a strong design for causal inference. The logic of the ITS closely parallels that of the RD design except that the threshold on the time rather than the baseline covariate is the basis for treatment assignment (Reichardt, 2006).
Interprofessional communication skills training to improve medical students' and nursing trainees' error communication ... - BMC Medical Education
Interprofessional communication skills training to improve medical students' and nursing trainees' error communication ....
Posted: Wed, 03 Jan 2024 08:00:00 GMT [source]
The Plant Design Studio is an industry pioneer with more than fifteen years of focused experience creating beautiful single-family and multifamily homes exclusively for prefabricated construction. Our team has designed more than 40 residential projects, earning some of the industry’s top honors. You should anticipate and incorporate those limitations into your conclusion, as well as the basic research design. Include a statement in your manuscript about any perceived limitations, and how you considered them while designing your experiment and drawing the conclusion.
Researchers want to see if their interventions will have some effect on a small group of people before they seek funding and dedicate time to conduct a true experiment. Broadly, preclinical research can be classified into two distinct categories depending on the aim and purpose of the experiment, namely, “hypothesis generating” (exploratory) and “hypothesis testing” (confirmatory) research (Fig. 1). Hypothesis generating studies are often scientifically-informed, curiosity and intuition-driven explorations which may generate testable theories regarding the pathophysiology of disease and potential drug targets.
Consequently, they are often used as stepping stones towards more rigorous research designs. As such, understanding pre-experimental designs is a fundamental part of the researcher’s toolkit, paving the way for more comprehensive and controlled investigations. Let’s say all the above parameters work just in favor of your experiment, you even have a control group to compare it with, but that still leaves us with one problem. It is possible that the subjects in your pre-experimental design were a lot different from the subjects you have for the true experiment. If this is the case, even if your treatment is constant, there is still going to be a change in your results. In this section, we will describe the major domains, in other words, sources that could contribute to experimental bias if not carefully considered and if mitigating tactics are not included in the design of hypothesis testing experiments before data collection starts.
A nearby sign informed customers that if the sales clerk did not ask them, they would get a lottery ticket for free. Observed differences between the two groups are assumed to be a result of the treatment. The team lead decides one group of employees to get the soft skills training while the other group remains as a control group and is not exposed to any program. He then compares both the groups and finds out the treatment group has evolved in their soft skills more than the control group.

No comments:
Post a Comment